Contact wire voltage
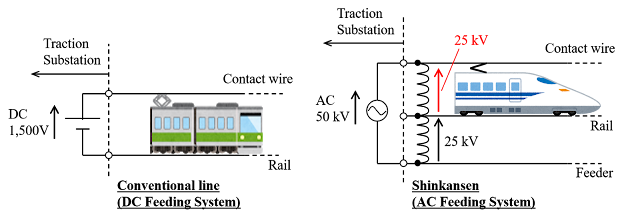
AC feeding voltage of a conventional line (which means "urban train without high-speed") is a single-phase AC voltage of 20 kV, but a standard voltage of the Shinkansen Overhead Contact Line is 50Hz AC voltage of 25 kV.
The main reasons for adopting an AC voltage of 25 kV as the standard voltage are as follows:
(1) With 1,500 V DC electrification, the collected current is large, the overhead contact line is thick, and the traction substation interval is 3 to 5 km, which means high construction costs.
(2) With 1,500 V DC electrification, the power collectors are heavy and tracking during high-speed operation is difficult.
(3) With 1,500 V DC electrification, selective shutting off a fault current is difficult because the fault current value and load current value are comparable.
(4) Because the Shinkansen is a new line, and tunnels and other facilities are newly provided, sufficient insulation clearance can be secured from the outset, and there are barely any problems in comparison with the 20 kV AC of a conventional line.
(5) Since the voltage drop is small in comparison with a 20 kV AC system, the TSS interval can also be long and there is more freedom to select power-receiving points.
(6) 25 kV AC is a global standard.
The main reasons for adopting an AC voltage of 25 kV as the standard voltage are as follows:
(1) With 1,500 V DC electrification, the collected current is large, the overhead contact line is thick, and the traction substation interval is 3 to 5 km, which means high construction costs.
(2) With 1,500 V DC electrification, the power collectors are heavy and tracking during high-speed operation is difficult.
(3) With 1,500 V DC electrification, selective shutting off a fault current is difficult because the fault current value and load current value are comparable.
(4) Because the Shinkansen is a new line, and tunnels and other facilities are newly provided, sufficient insulation clearance can be secured from the outset, and there are barely any problems in comparison with the 20 kV AC of a conventional line.
(5) Since the voltage drop is small in comparison with a 20 kV AC system, the TSS interval can also be long and there is more freedom to select power-receiving points.
(6) 25 kV AC is a global standard.


Comments
Post a Comment